Android Network Packet Capture: Complete Guide with tcpdump and Wireshark
🚀 Android Network Packet Capture Overview
Network packet analysis is one of the most valuable debugging techniques for mobile development. While iOS development offers straightforward packet capture with rvictl -s [UUID], Android requires a different approach. This guide will teach you how to capture and analyze network packets on Android devices using tcpdump and Wireshark.
What You’ll Learn:
- 📱 Android packet capture setup with tcpdump
- 🔍 Network traffic analysis using Wireshark
- 🛠️ Debugging techniques for connectivity issues
- 📊 Real-world troubleshooting examples
- 🔧 Alternative methods for non-rooted devices
🎯 Why Network Packet Analysis Matters
Common Use Cases:
- API Integration Issues - Debug backend communication problems
- Streaming Problems - Analyze RTSP/RTMP connection failures
- Third-party Library Issues - Understand library network behavior
- Performance Optimization - Identify network bottlenecks
- Security Analysis - Monitor data transmission patterns
Benefits of Packet Analysis:
- ✅ Uncover hidden issues that logs don’t reveal
- ✅ Real-time network monitoring for live debugging
- ✅ Protocol-level insights into communication problems
- ✅ Cross-platform compatibility verification
- ✅ Performance bottleneck identification
📋 Prerequisites and Requirements
Required Tools:
- Rooted Android device (recommended for full access)
- tcpdump binary for Android
- Wireshark for packet analysis
- ADB (Android Debug Bridge) for device communication
Optional Tools:
- tPacketCapture - Alternative for non-rooted devices
- NetworkMiner - Advanced packet analysis
- Ettercap - Network security analysis
⚠️ Important Note: While non-rooted devices can use VPN-based solutions like tPacketCapture, these methods may miss packets and aren’t recommended for critical debugging.
🛠️ Step-by-Step Setup Guide
Step 1: Download tcpdump for Android
Download the appropriate tcpdump binary for your Android architecture:
# Check your device architecture
adb shell getprop ro.product.cpu.abi
# Download tcpdump based on architecture
# For ARM64: https://www.androidtcpdump.com/android-tcpdump/downloads/4.99.3/tcpdump
# For ARM: https://www.androidtcpdump.com/android-tcpdump/downloads/4.99.3/tcpdump
Step 2: Transfer tcpdump to Android Device
# Push tcpdump to device
adb push tcpdump /data/local/tcpdump
If you encounter permission errors:
# Get root access temporarily
adb root
adb push tcpdump /data/local/tcpdump
adb unroot
Step 3: Set Up tcpdump Permissions
# Connect to device shell
adb shell
# Switch to root user
su
# Navigate to tcpdump location
cd /data/local
# Make tcpdump executable
chmod a+x tcpdump
# Verify installation
./tcpdump --version
📡 Capturing Network Packets
Basic Packet Capture
Start capturing packets with basic settings:
# Basic capture on all interfaces
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/capture.pcap
Command Parameters Explained:
-
-i any: Capture on all network interfaces -
-p: Don’t put interface in promiscuous mode -
-s 0: Capture full packet (no size limit) -
-w /sdcard/capture.pcap: Write to file
Advanced Capture Options
Capture Specific Interface:
# Capture only WiFi traffic
./tcpdump -i wlan0 -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/wifi_capture.pcap
# Capture only mobile data
./tcpdump -i rmnet_data0 -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/mobile_capture.pcap
Filter by Protocol:
# Capture only HTTP/HTTPS traffic
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/http_capture.pcap port 80 or port 443
# Capture only TCP traffic
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/tcp_capture.pcap tcp
# Capture specific host
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/host_capture.pcap host 192.168.1.100
Capture with Size Limits:
# Capture with packet size limit
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 1500 -w /sdcard/limited_capture.pcap
# Capture with file size rotation
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -W 5 -C 10 -w /sdcard/capture_%d.pcap
Real-time Monitoring
Monitor packets in real-time without saving to file:
# Display packets in real-time
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0
# Verbose output with packet details
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -v
# Very verbose output
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -vvv
📊 Transferring and Analyzing Packets
Transfer Capture File to Computer
# Pull capture file from device
adb pull /sdcard/capture.pcap
# Pull with custom filename
adb pull /sdcard/capture.pcap android_capture_$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S).pcap
Open in Wireshark for Analysis
- Launch Wireshark
- Open the .pcap file
- Apply filters for specific analysis
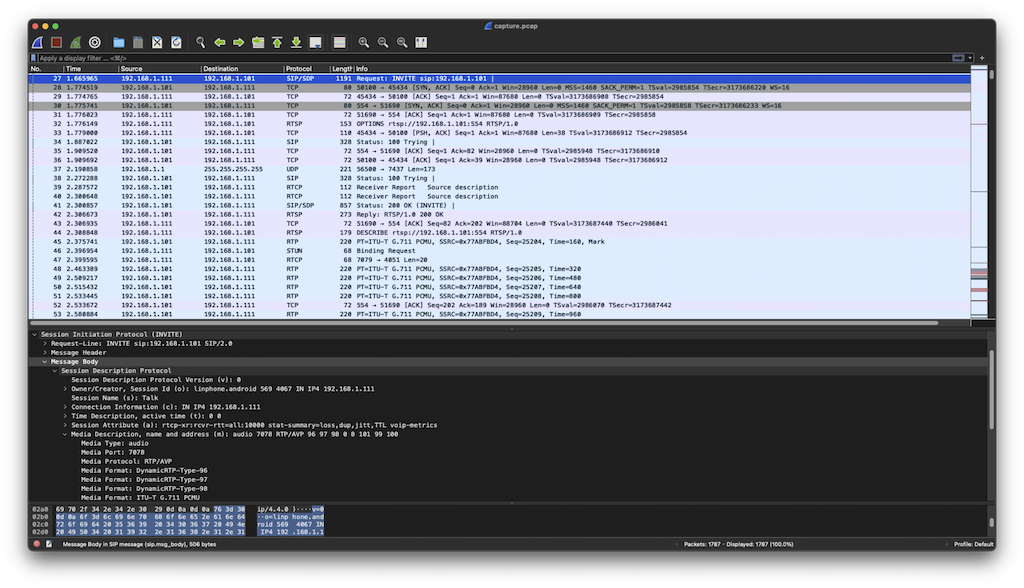
Useful Wireshark Filters
# HTTP traffic only
http
# HTTPS traffic
ssl or tls
# Specific IP address
ip.addr == 192.168.1.100
# Specific port
tcp.port == 8080
# TCP connection issues
tcp.flags.syn == 1 and tcp.flags.ack == 0
# DNS queries
dns
# Failed connections
tcp.flags.reset == 1
🔧 Alternative Methods for Non-Rooted Devices
Method 1: tPacketCapture (VPN-based)
# Install from Google Play Store
# https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=jp.co.taosoftware.android.packetcapture
Limitations:
- ❌ May miss packets due to VPN routing
- ❌ Limited to user-level applications
- ❌ Performance impact on device
- ❌ Not suitable for system-level debugging
Method 2: Network Proxy Setup
# Set up proxy on device
Settings > Wi-Fi > Advanced > Proxy
# Use computer as proxy
# Capture packets on computer instead
Method 3: ADB Port Forwarding
# Forward device traffic through computer
adb forward tcp:8080 tcp:8080
# Capture on computer's network interface
tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w capture.pcap port 8080
🚨 Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue 1: Permission Denied
# Solution: Ensure proper permissions
adb shell
su
chmod 755 /data/local/tcpdump
chown root:root /data/local/tcpdump
Issue 2: No Packets Captured
# Check if device is rooted
adb shell
su
# If no root access, use alternative methods
# Verify network interfaces
./tcpdump -D
# Test with specific interface
./tcpdump -i wlan0 -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/test.pcap
Issue 3: File System Full
# Check available space
adb shell df /sdcard
# Use external storage
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w /storage/emulated/0/capture.pcap
# Limit capture size
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -C 10 -w /sdcard/capture.pcap
Issue 4: ADB Connection Issues
# Restart ADB server
adb kill-server
adb start-server
# Check device connection
adb devices
# Enable USB debugging
# Settings > Developer options > USB debugging
📈 Real-World Debugging Examples
Example 1: RTSP Streaming Issues
Problem: RTSP stream disconnects after 1 minute
Solution:
# Capture RTSP traffic
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/rtsp_capture.pcap port 554
# Analysis revealed missing GET_PARAMETER keep-alive packets
# Fixed by implementing proper RTSP keep-alive mechanism
Example 2: API Timeout Issues
Problem: API calls timeout randomly
Solution:
# Capture API traffic
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/api_capture.pcap port 443
# Analysis showed TCP connection resets
# Identified network configuration issues
Example 3: Third-party Library Problems
Problem: Library not responding to network requests
Solution:
# Capture all traffic during library usage
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/library_capture.pcap
# Analysis revealed unexpected protocol behavior
# Modified library configuration accordingly
🔒 Security Considerations
Privacy and Legal Compliance
- ✅ Only capture your own traffic or authorized network traffic
- ✅ Respect privacy laws and regulations
- ✅ Secure captured files containing sensitive data
- ✅ Delete capture files after analysis
- ✅ Use in controlled environments only
Best Practices
# Use specific filters to limit capture scope
./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/capture.pcap host 192.168.1.100
# Set capture time limits
timeout 300 ./tcpdump -i any -p -s 0 -w /sdcard/capture.pcap
# Use encrypted storage for sensitive captures
# Store captures in encrypted directory
🔗 Related Articles
- iOS Network Packet Capture
- P2P Technology Fundamentals
- STUN/TURN/ICE Protocols
- WebRTC Implementation
✅ Conclusion
Network packet analysis is an invaluable debugging technique that can save hours of troubleshooting time. By mastering tcpdump and Wireshark on Android, you can:
Key Benefits Achieved:
- 🔍 Deep network insights that logs can’t provide
- 🚀 Faster problem resolution through protocol-level analysis
- 📊 Performance optimization through traffic analysis
- 🛡️ Security verification of data transmission
- 🔧 Cross-platform debugging capabilities
Best Practices:
- Use specific filters to focus on relevant traffic
- Capture in controlled environments for accurate results
- Analyze packets systematically using Wireshark filters
- Document findings for future reference
- Respect privacy and security guidelines
💡 Pro Tip: When logs are silent and console output is empty, network packets always tell the truth. Mastering packet capture can save you 10x the debugging time.
💡 Pro Tip: Consider using automated packet capture scripts for continuous monitoring during development and testing phases.
🔔 Stay Updated: Follow our network analysis series for more advanced debugging techniques!
📚 Additional Resources:
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: