Jenkins Server Setup: Complete Docker Installation Guide
🚀 Jenkins Server Setup Overview
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through setting up a Jenkins server using Docker containers. This approach is not only simple and fast but also ensures environment consistency across different deployments.
What You’ll Learn:
- 🐳 Docker-based Jenkins installation for consistency
- 🔧 Step-by-step setup process with detailed instructions
- 📱 Android build environment integration
- 🛡️ Best practices for production deployment
- 🔍 Troubleshooting common setup issues
🎯 Why Use Docker for Jenkins Setup?
Benefits of Docker-Based Jenkins:
- ✅ Environment Consistency - Same setup across development, staging, and production
- ✅ Easy Deployment - Quick setup and teardown
- ✅ Version Control - Specific Jenkins versions for different projects
- ✅ Resource Isolation - No conflicts with other applications
- ✅ Scalability - Easy to replicate for multiple environments
Available Jenkins Images:
- Standard Jenkins:
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17 - Android-Enabled Jenkins:
ghcr.io/nickhuangcyh/docker-jenkins-and-android-env:v1.0.0-jdk17
🛠️ Step-by-Step Jenkins Setup
Step 1: Pull Docker Image
First, we need to pull the Jenkins Docker image from GitHub Container Registry. Open your terminal and execute one of the following commands:
Option A: Standard Jenkins Environment
docker pull jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
Option B: Jenkins with Android Build Environment
docker pull ghcr.io/nickhuangcyh/docker-jenkins-and-android-env:v1.0.0-jdk17
Image Comparison: | Image | Description | Use Case | |——-|————-|———-| | jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17 | Standard Jenkins with JDK 17 | General CI/CD pipelines | | ghcr.io/nickhuangcyh/docker-jenkins-and-android-env:v1.0.0-jdk17 | Jenkins + Android SDK + Build tools | Android app development |
Step 2: Run Jenkins Container
Next, we’ll run the Jenkins container. Make sure to replace ${volume_path} with your desired local path for Jenkins data storage.
Option A: Standard Jenkins Container
docker run -d \
--name jenkins-server \
-v ${volume_path}:/var/jenkins_home \
-p 8080:8080 \
-p 50000:50000 \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
Option B: Android-Enabled Jenkins Container
docker run -d \
--name jenkins-android-server \
-v ${volume_path}:/var/jenkins_home \
-p 8080:8080 \
-p 50000:50000 \
ghcr.io/nickhuangcyh/docker-jenkins-and-android-env:v1.0.0-jdk17
Command Explanation:
-
-d: Run container in detached mode (background) -
--name: Assign a name to the container for easy management -
-v: Mount local directory to container’s Jenkins home -
-p 8080:8080: Map container port 8080 to host port 8080 (Web UI) -
-p 50000:50000: Map container port 50000 to host port 50000 (Agent communication)
Step 3: Access Jenkins Web Interface
After the container starts, you can access Jenkins through your browser at http://localhost:8080. On first access, you’ll be prompted to enter the initial administrator password.
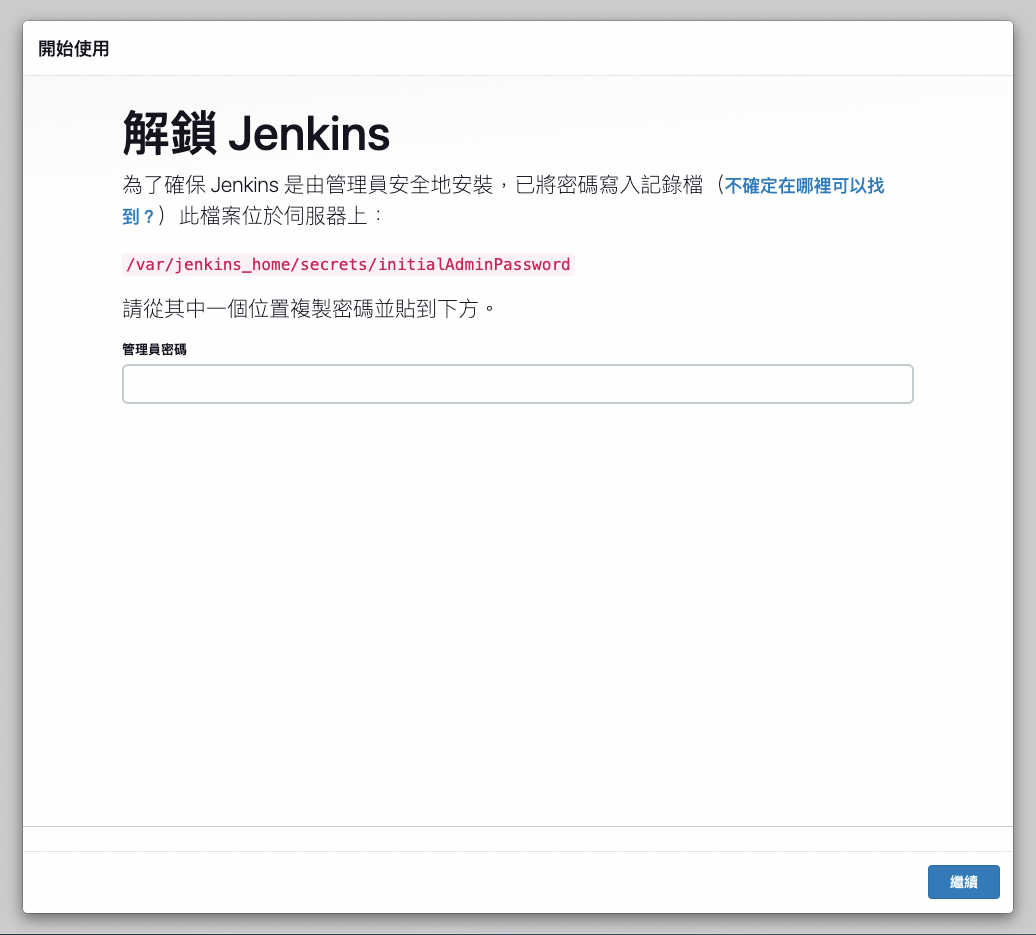
Finding the Initial Password
💡 Pro Tip: Remember the
${volume_path}we set during container creation? You can find the initial password at:cat ${volume_path}/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Alternative Methods to Get Password:
# Method 1: Check container logs
docker logs jenkins-server
# Method 2: Execute command inside container
docker exec jenkins-server cat /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword
# Method 3: Direct file access (if volume is mounted)
cat ${volume_path}/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Step 4: Complete Initial Setup
- Enter the initial password from the previous step
- Install recommended plugins or choose custom installation
- Create admin user with secure credentials
- Configure Jenkins URL (use
http://localhost:8080for local setup) - Start using Jenkins! 🎉
🔧 Advanced Configuration Options
Custom Docker Run Command with Additional Options
docker run -d \
--name jenkins-server \
--restart unless-stopped \
-v jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
-v /usr/bin/docker:/usr/bin/docker \
-p 8080:8080 \
-p 50000:50000 \
-e JAVA_OPTS="-Djenkins.install.runSetupWizard=false" \
-e JENKINS_OPTS="--prefix=/jenkins" \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
Advanced Options Explained:
-
--restart unless-stopped: Automatically restart container on system reboot -
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock: Enable Docker-in-Docker capabilities -
-e JAVA_OPTS: Customize JVM options -
-e JENKINS_OPTS: Customize Jenkins startup options
Docker Compose Setup
Create a docker-compose.yml file for easier management:
version: "3.8"
services:
jenkins:
image: jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
container_name: jenkins-server
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "8080:8080"
- "50000:50000"
volumes:
- jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
environment:
- JAVA_OPTS=-Djenkins.install.runSetupWizard=false
networks:
- jenkins-network
volumes:
jenkins_home:
networks:
jenkins-network:
driver: bridge
Start with Docker Compose:
docker-compose up -d
🚨 Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue 1: Container Won’t Start
# Check container status
docker ps -a
# View container logs
docker logs jenkins-server
# Common solutions:
# 1. Port already in use
sudo lsof -i :8080
# 2. Permission issues with volume
sudo chown -R 1000:1000 ${volume_path}
Issue 2: Can’t Access Jenkins Web UI
# Check if container is running
docker ps
# Verify port mapping
docker port jenkins-server
# Test connectivity
curl http://localhost:8080
Issue 3: Permission Denied Errors
# Fix volume permissions
sudo chown -R 1000:1000 ${volume_path}
# Or run container with different user
docker run -d \
--name jenkins-server \
-v ${volume_path}:/var/jenkins_home \
-p 8080:8080 \
-p 50000:50000 \
--user root \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
Issue 4: Out of Memory Errors
# Increase container memory limit
docker run -d \
--name jenkins-server \
--memory=2g \
--memory-swap=4g \
-v ${volume_path}:/var/jenkins_home \
-p 8080:8080 \
-p 50000:50000 \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
📊 Performance Optimization
Resource Recommendations
| Environment | CPU | Memory | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Development | 1 core | 2GB | 10GB |
| Testing | 2 cores | 4GB | 20GB |
| Production | 4+ cores | 8GB+ | 50GB+ |
JVM Tuning
# Optimize JVM settings for production
docker run -d \
--name jenkins-server \
-v ${volume_path}:/var/jenkins_home \
-p 8080:8080 \
-p 50000:50000 \
-e JAVA_OPTS="-Xmx4g -Xms2g -XX:+UseG1GC" \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
🔒 Security Best Practices
1. Use HTTPS in Production
# Mount SSL certificates
docker run -d \
--name jenkins-server \
-v ${volume_path}:/var/jenkins_home \
-v /path/to/ssl:/var/jenkins_ssl \
-p 443:8080 \
-e JENKINS_OPTS="--httpPort=-1 --httpsPort=8080 --httpsCertificate=/var/jenkins_ssl/cert.pem --httpsPrivateKey=/var/jenkins_ssl/key.pem" \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
2. Implement Authentication
- Use LDAP/Active Directory integration
- Enable Jenkins security features
- Regular password updates
- Two-factor authentication (if available)
3. Network Security
# Use custom network with firewall rules
docker network create --driver bridge --subnet=172.20.0.0/16 jenkins-network
docker run -d \
--name jenkins-server \
--network jenkins-network \
--ip 172.20.0.2 \
-v ${volume_path}:/var/jenkins_home \
-p 8080:8080 \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
📈 Monitoring and Maintenance
Health Checks
# Add health check to container
docker run -d \
--name jenkins-server \
--health-cmd="curl -f http://localhost:8080 || exit 1" \
--health-interval=30s \
--health-timeout=10s \
--health-retries=3 \
-v ${volume_path}:/var/jenkins_home \
-p 8080:8080 \
-p 50000:50000 \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
Backup Strategy
# Create backup script
#!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/backup/jenkins"
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
# Stop Jenkins container
docker stop jenkins-server
# Create backup
tar -czf "${BACKUP_DIR}/jenkins_backup_${DATE}.tar.gz" -C ${volume_path} .
# Start Jenkins container
docker start jenkins-server
echo "Backup completed: jenkins_backup_${DATE}.tar.gz"
🔗 Related Articles
- What is Jenkins?
- Jenkins SSH Credentials Configuration
- GitHub Container Registry Setup
- macOS Development Environment
✅ Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully set up a Jenkins server using Docker. This approach provides:
Key Benefits Achieved:
- 🚀 Quick deployment with Docker containers
- 🔧 Environment consistency across different setups
- 📱 Android development support (with custom image)
- 🛡️ Easy backup and restore capabilities
- 📈 Scalable architecture for team growth
Next Steps:
- Configure your first pipeline in Jenkins
- Set up build agents for distributed builds
- Integrate with version control systems
- Implement security measures for production use
- Set up monitoring and alerting
💡 Pro Tip: Use Docker Compose for easier Jenkins management in development environments, and consider implementing automated backups for production deployments.
💡 Pro Tip: Consider using Jenkins Blue Ocean plugin for a more modern and intuitive pipeline visualization experience.
🔔 Stay Updated: Follow our DevOps series for more CI/CD and automation insights!
📚 Additional Resources:
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: